LAF, Airlock, and Fume Hoods

Maintaining precise standards of cleanliness and security is vital in controlled environments such as pharmaceutical facilities, and laboratories. Devices such as Fume Hoods, Airlocks, and Laminar Air Flow (LAF) units are essential in this situation. Each has a specific function and functions differently to maintain ideal circumstances for diverse applications.
Laminar Air Flow (LAF)
Laminar Air Flow units (LAFs) are equipment designed to provide a continuous stream of filtered air in a unidirectional flow. This creates a highly controlled, particle-free environment suitable for tasks requiring minimal contamination.
Operation
To eliminate pollutants, a Laminar Air Flow (LAF) system draws air from the surrounding area and filters it through pre-filters and High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters. This filtered air is then produced in a continuous, unidirectional flow—which can be horizontal or vertical—by blowers or fans. This laminar flow sweeps away particles and keeps the area sterile as it flows smoothly and parallel to the work surface. This continuous flow guarantees that the work area in LAF workstations or cleanrooms stays free of particulate contamination, offering a controlled, clean environment that is essential for many applications in laboratories, industry, and healthcare centers.
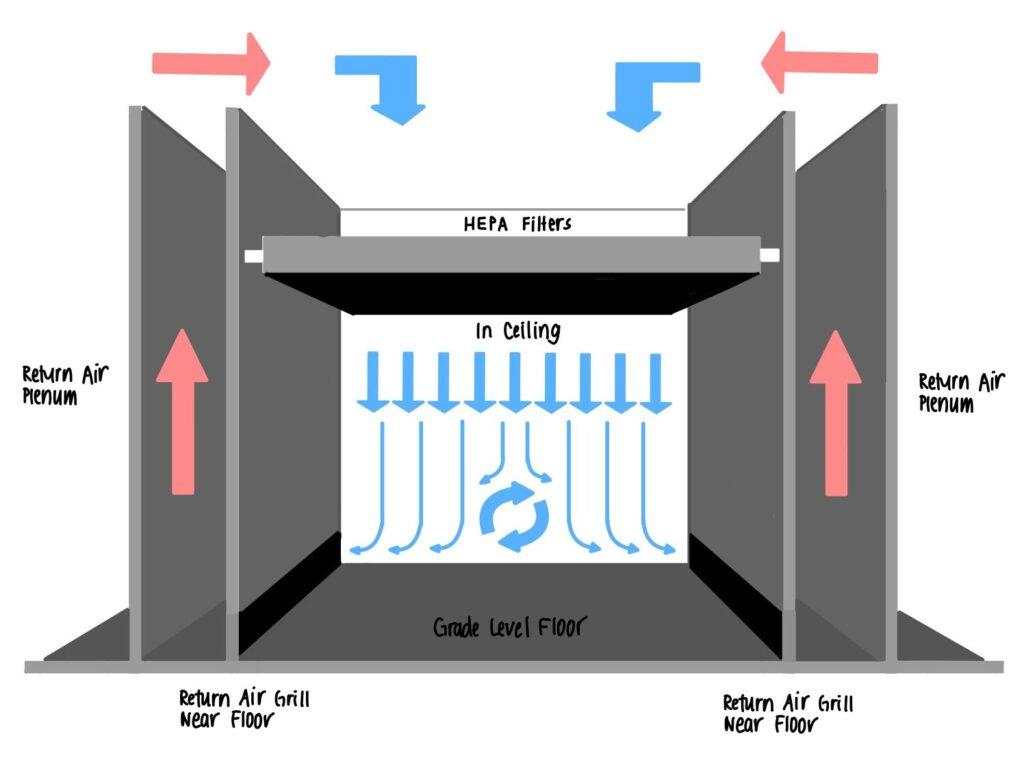
Applications
To prevent sample and staff contamination, LAF workstations are utilized in biotechnological, pharmaceutical, and microbiological operations. LAF systems make guarantee that delicate parts and goods are created in a dust- and particle-free environment in manufacturing, especially in the semiconductor, aerospace, and medical device industries. LAF systems are essential in operating rooms and isolation units of healthcare facilities to avoid infection and guarantee patient safety.
Airlock (Cleanroom Antechamber)
An airlock is a controlled environment chamber with two or more doors. It is often referred to as a cleanroom antechamber or vestibule. It serves as a transitional area between several cleaning zones, avoiding cross-contamination.
Operation
To reduce contamination when personnel or materials come in and go out of cleanrooms and other controlled environments, airlocks are controlled entryways. An airlock separates places with varying degrees of cleanliness by means of two interlocking doors that are incapable of being opened simultaneously. To prevent contaminants from entering the cleaner area, the first door closes before the second door opens when approaching from a less clean region. To remove particles from personnel or materials, the airlock is usually fitted with air showers, HEPA filters, or other decontamination devices. By stopping the transmission of contaminants, this procedure serves to maintain the cleanroom’s integrity by guaranteeing that the controlled environment is free of pollutants and particles.
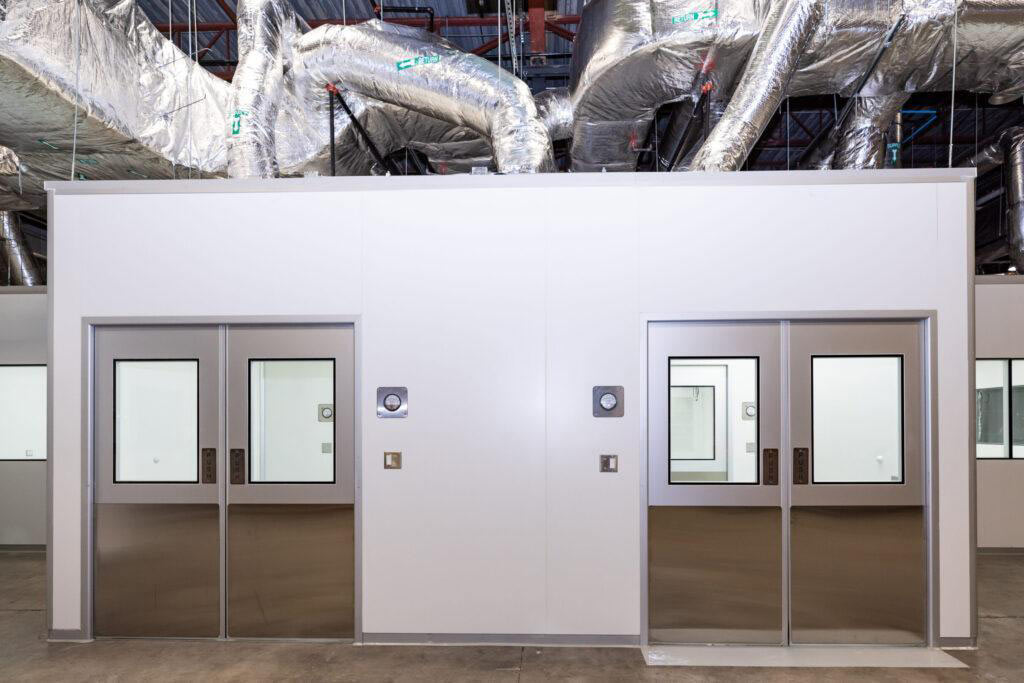

Applications
In situations where keeping a contaminant-free environment is essential, airlocks are indispensable. Airlocks keep dust, bacteria, and other particles out of cleanrooms used for biotechnology research, pharmaceutical manufacture, and semiconductor fabrication. These particles could jeopardize delicate procedures. By preventing microorganisms from entering sterile spaces, airlocks in healthcare settings—like hospitals and laboratories—help limit infection. To maintain controlled settings for the assembly and testing of critical equipment, airlocks are widely utilized in the aerospace and defense industries. Furthermore, airlocks in hazardous environments—like nuclear power plants and chemical factories—make sure that dangerous materials do not leak into uncontaminated areas, safeguarding both the surrounding environment and people.
Fume Hood
A ventilated container called a fume hood is used to collect and eliminate dangerous dusts, vapors, or fumes that are produced during chemical procedures or tests. They shield the environment and its occupants from dangerous chemical exposure.
Operation
A fume hood is a ventilated enclosure used in laboratories to safely manage hazardous or volatile chemicals by drawing in air from the laboratory and expelling it outside, thus preventing the escape of harmful vapors, fumes, and dust. The operation of a fume hood involves a sash, which is a movable glass barrier that provides a physical barrier between the user and the chemicals while also controlling the airflow. Air is drawn in through the front opening of the hood, passing through a series of baffles that direct the airflow, ensuring that contaminants are captured and exhausted efficiently. The air is then passed through filters, such as HEPA or activated carbon, before being expelled outside the building, ensuring that the laboratory environment remains safe for users. Proper use and maintenance of the fume hood, including keeping the sash at the recommended height and ensuring unobstructed airflow, are essential for its effective operation and the safety of laboratory personnel.
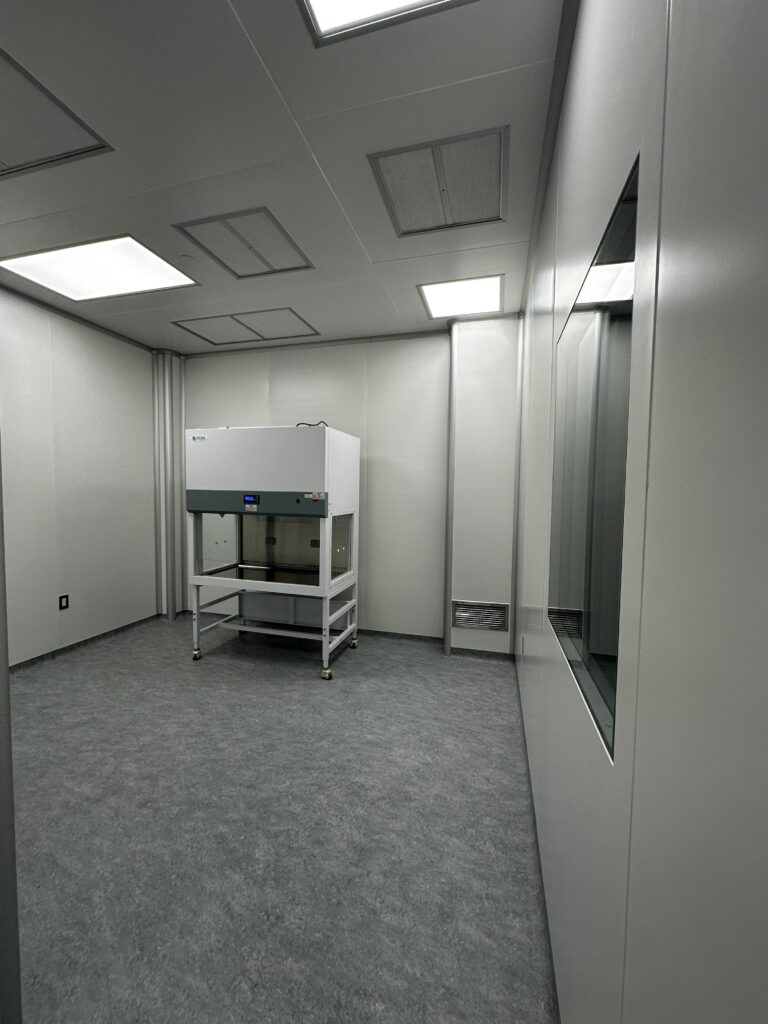

Applications
Assuring worker safety when managing dangerous materials in a variety of laboratory settings requires the use of fume hoods. Through containment and exhaustion outside the structure, they shield researchers working in chemical laboratories from harmful vapors, dust, and fumes. Fume hoods are employed in biotechnology and pharmaceutical facilities to protect workers from potentially harmful chemicals when synthesizing and testing novel substances. Fume hoods are utilized by forensic and environmental laboratories to securely examine items that can leak toxic materials. Fume hoods also give students doing experiments with volatile substances a safe space to work at educational facilities. Fume hoods serve an important part in keeping a safe and legal laboratory environment by regulating airflow and offering a physical barrier.

Key Differences
| Function | Operation | Applications | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAF | provide a particle-free environment for sensitive operations | filter air to create a clean workspace | sterile environments |
| Airlocks | manage differential pressures to prevent contamination between different cleanroom zones | manage air pressure differentials | maintaining cleanliness zones |
| Fume Hoods | protect against hazardous chemical exposures | capture and remove hazardous substances | chemical safety |
In conclusion, LAFs, Airlocks, and Fume Hoods are critical elements in settings where safety, cleanliness, and contamination control are of utmost importance. Each contributes in a unique way to the overall effectiveness and safety of different industrial and scientific operations by making sure that operational needs are met.
Ready to Master Cleanroom Excellence? Connect with us to stay ahead in cleanroom technology and safety standards.
GET IN TOUCH
Complete the form below to get in touch with our team.
