Manometers and Magnehelic Gauges
Manometers and Magnehelic Gauges are two types of pressure measuring instruments commonly used in various industries and applications, including cleanrooms. Cleanrooms provide a controlled environment; pressure, temperature, and humidity being the most critical factors to control.
Different industries have different requirements when it comes to controlling parameters. In cleanroom applications, pressure is the most critical parameter to control when maintaining GMP classifications for the product being manufactured.
There are three types of pressure measurements:
- Positive pressure is the one that is greater than atmospheric pressure.
- Negative pressure is less than atmospheric.
- Differential pressure is the difference between positive and negative pressures.
Manometers
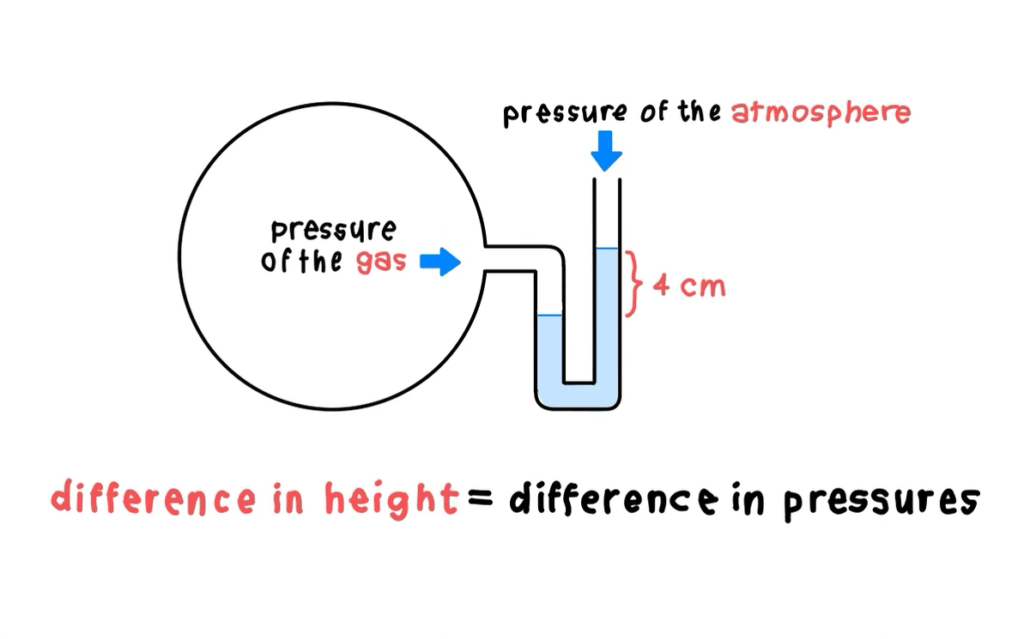
A manometer is a device used to measure fluid pressure, including static pressure, velocity, leakage, filter resistance, and gas pressure. Most commonly, manometers are used to measure liquid and gas pressure.
Manometers typically consist of a U-shaped tube partially filled with a liquid, such as water or mercury. The pressure being measured is applied to one side of the U-tube, causing the liquid in the tube to move and create a pressure difference between the two arms of the tube. The height difference between the liquid levels in the two arms of the tube indicates the pressure being measured.
Types of Manometers

1. Simple Manometer
This is the basic form of a manometer with a U-shaped tube containing the liquid. It provides a direct measurement of pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Simple manometers also measure the differential pressure by stabilizing the weight of a liquid between two pressures.
If there is no pressure, the fluid will stay in the middle of the tube. The fluid moves when the pressure is higher on one side of the tube. Simple manometers can be beneficial because they don’t require a power supply.
2. Differential Manometer
A differential manometer is used to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system. It has two arms connected to separate pressure sources, and the height difference between the liquid levels represents the pressure difference.
3. Inclined Manometer
In an inclined manometer, the U-tube is inclined at an angle, which allows for more accurate readings by increasing the sensitivity and resolution of the instrument.
4. Digital Manometer
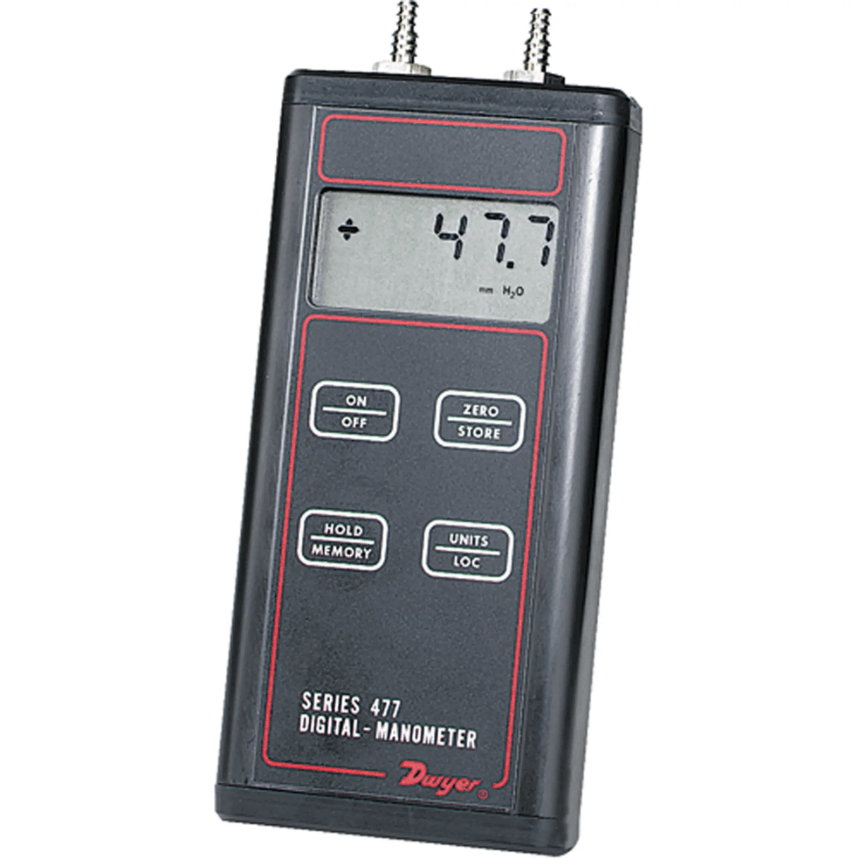

This type of manometers use a sensor or transducer to determine pressure instead of fluid. Sensors and transducers transform observed pressure levels into an electric signal. Technicians then use the signal to understand the pressure.
Unlike the simple version, digital manometers are more portable and easier to carry. It is also easier to read the result, providing precise results. Another benefit of a digital manometer is that the data collected can be recorded and transmitted to a computer via Bluetooth or cables.
Magnehelic Gauges
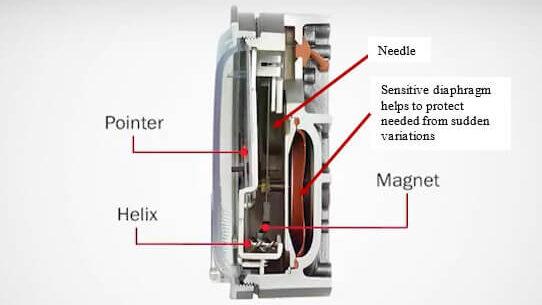
The Magnehelic gauge is a specific type of manometer manufactured by Dwyer Instruments. It uses a diaphragm and a magnet to measure and indicate pressure differentials. The diaphragm is sensitive to pressure variations and flexes accordingly. As the diaphragm moves, it changes the position of a magnet, which, in turn, rotates a pointer on a scale to provide pressure readings.
Magnehelic gauges are commonly used for measuring low differential pressures in ventilation systems, cleanrooms, air filters, and other HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) applications. They are known for their accuracy, reliability, and ease of use. These gauges are available in different pressure ranges and can be customized with various options to suit specific requirements (ranging from -3000 to +8000 pascals).
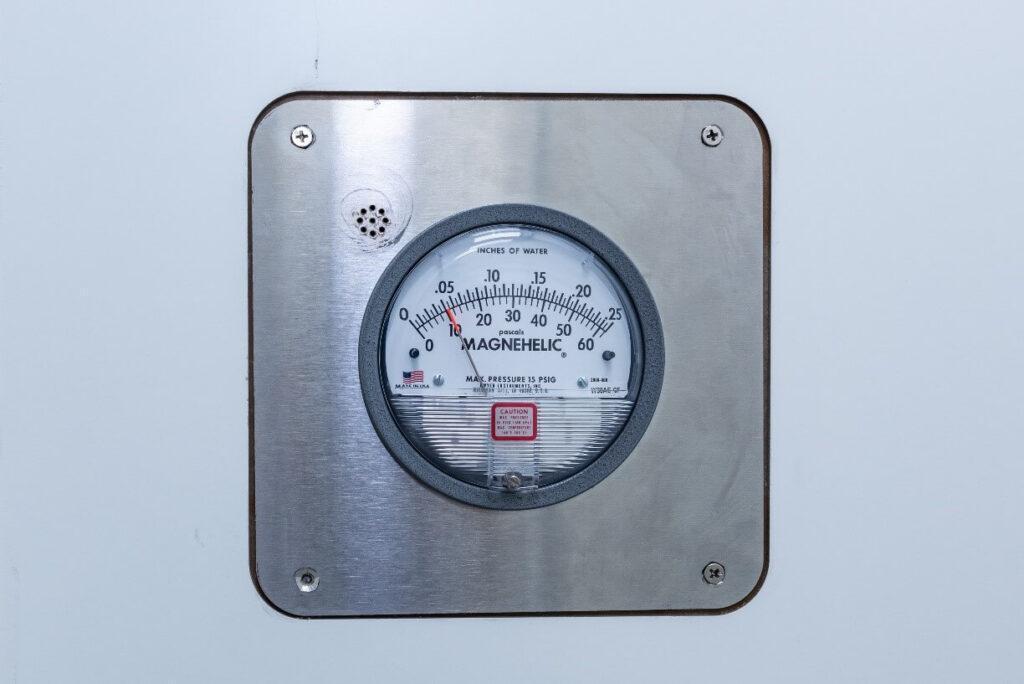

Magnehelic gauges are better than most other gauges because they eliminate problems like backlash, excessive wear, and toxicity. In addition, it is considered to be one of the most accurate tools to measure pressure with an accuracy of +/- 2%.
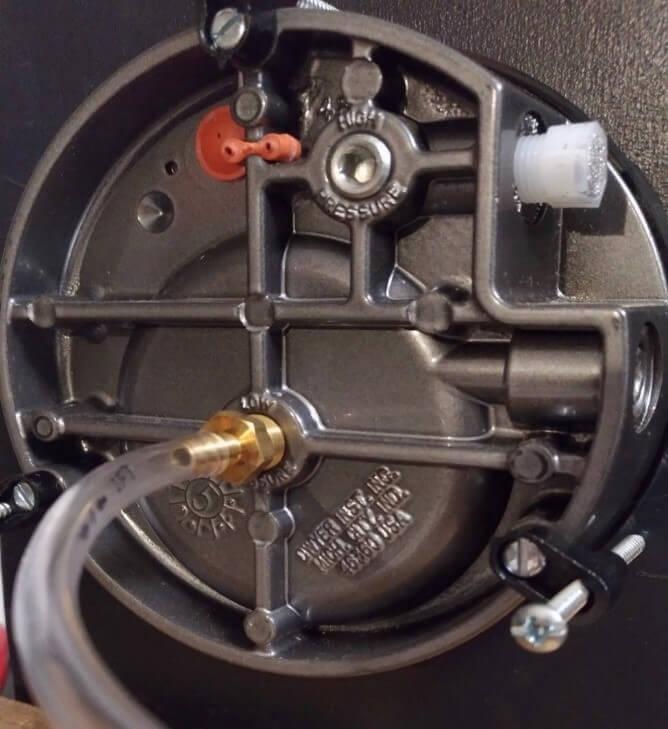

No matter the location, the gauge must be zeroed as a final step to be used in the position installed. If zeroing is done before the installation, the reading may be inaccrate as they will vary more than 2%. You can move the gauge from place to place, but it has to be zeroed every time it is relocated.
To choose the best manometer or magnehelic gauge for you, make sure to understand which measurements you’ll be reading most. Get in touch with our team to learn more and choose the perfect fit for your needs.

| Comparison between | Analog Gauges | Digital Gauges | ||
| Features | Analog Gauges | Digital Gauges | ||
| Display | Needle on dial | Digital readout | ||
| Accuracy | Moderate; can drift over time | High; precise readings | ||
| Ease of Use | Simple, no power required | Easy to read; may require power/battery | ||
| Calibration | Manual; requires pressure source | Often auto-calibration or manual with software | ||
| Durability | Rugged, fewer electronics | Sensitive to harsh environments, but compact | ||
| Data Logging | None | Can log measurements, alarms, and trends | ||
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, potentials long-term savings | ||
When selecting a cleanroom pressure gauge, both analog and digital options have distinct advantages. Analog gauges are rugged, simple, and ideal for environments where durability is critical. Digital gauges offer higher accuracy, built-in data logging, and modern connectivity, making them suitable for regulated cleanrooms that require precise differential pressure monitoring. Regardless of the type, proper calibration is essential.
Calibration Steps for Magnehelic and Differential Pressure Gauges
- Preparation: Ensure the gauge is clean and at room temperature; verify the reference pressure source is calibrated.
- Zero Adjustment: Close all connections; adjust the zero knob (analog) or menu option (digital) until the display reads zero.
- Apply Known Pressure: Use a calibrated pressure source to apply a standard value; compare the reading to the reference.
- Adjust Reading: Analog: turn the adjustment screw; Digital: use calibration function/software.
- Repeat & Verify: Test multiple points; document readings for compliance and maintenance.
Note: Regular calibration ensures reliable pressure monitoring in critical cleanroom environments.
GET IN TOUCH
Complete the form below to get in touch with our team.
